一聚合操作
groupByrollupcubepivotRelationalGroupedDataset上的聚合操作
1自定义udf与udaf
1 | package com.nicai.www |
2 聚合
groupBy 算子会按照列将 Dataset 分组, 并返回一个 RelationalGroupedDataset 对象, 通过 RelationalGroupedDataset 可以对分组进行聚合
1 | package com.nicai.www |
3 多维聚合
我们可能经常需要针对数据进行多维的聚合, 也就是一次性统计小计, 总计等, 一般的思路如下
1 | class DuoWeiJuHe { |
4 连接 与广播连接
连接分为两种
- 无类型连接
join - 连接类型
Join Types
1 | 1 cross 交叉连接 笛卡尔积 全连接* 交叉连接是一个非常重的操作, 在生产中, 尽量不要将两个大数据集交叉连接, 如果一定要交叉连接, 也需要在交叉连接后进行过滤, 优化器会进行优化 |
1 |
|
广播连接
Join 会在集群中分发两个数据集, 两个数据集都要复制到 Reducer 端, 是一个非常复杂和标准的 ShuffleDependency
优化:
Map 端 Join 之所以说它效率很低, 原因是需要在集群中进行数据拷贝, 如果能减少数据拷贝, 就能减少开销
可以将小数据集收集起来, 分发给每一个 Executor, 然后在需要 Join 的时候, 让较大的数据集在 Map 端直接获取小数据集, 从而进行 Join, 这种方式是不需要进行 Shuffle 的, 所以称之为 Map 端 Join
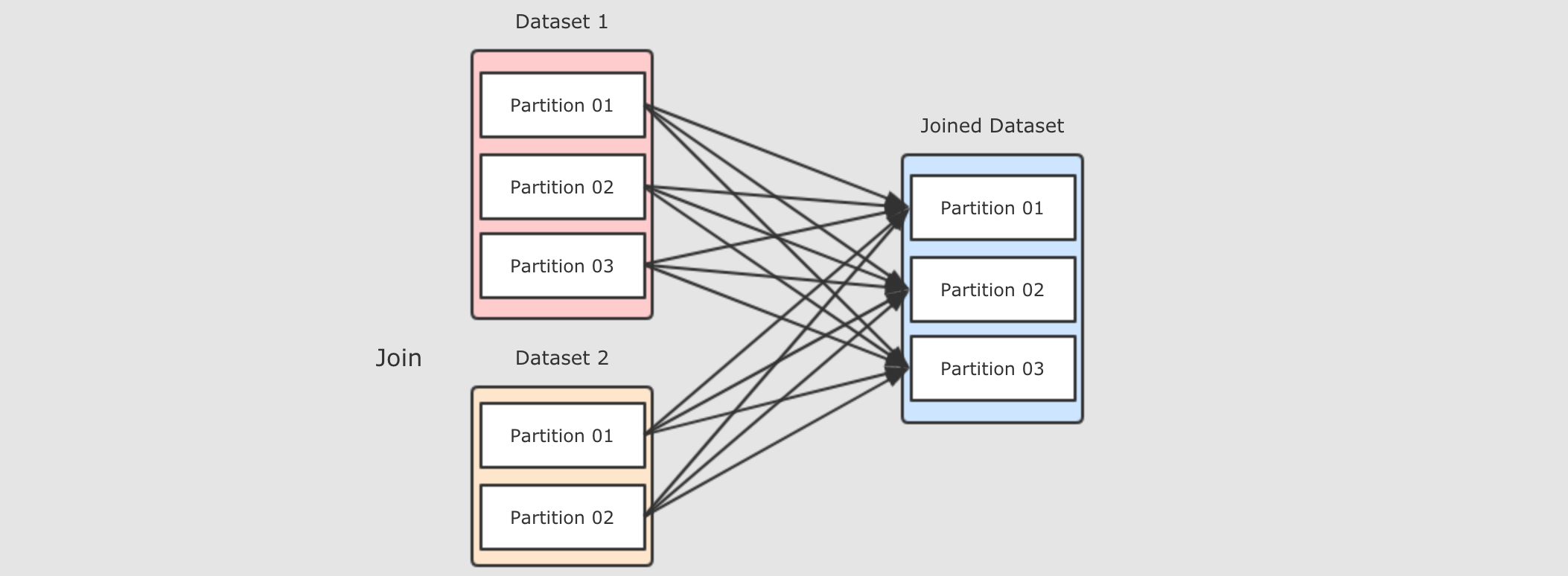
正常join图:
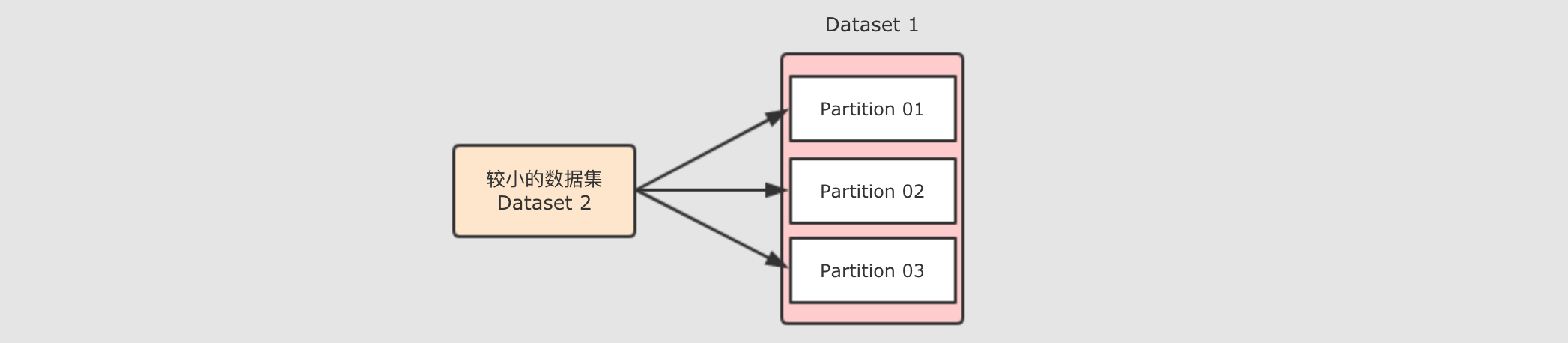
开启mapjoin图
1 | //广播连接 |
1 使用 Dataset 实现 Join 的时候会自动进行 Map 端 Join
1 | 自动进行 Map 端 Join 需要依赖一个系统参数 spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold, 当数据集小于这个参数的大小时, 会自动进行 Map 端 Join |
2 也可以使用函数强制开启 Map 端 Join
1 | 在使用 Dataset 的 join 时, 可以使用 broadcast 函数来实现 Map 端 Join |
5 窗口函数
1 | 窗口函数 解决了 在一个大的数据集里 进行分组 求前几个等需求 |
1 | package com.nicai.www |
问题1:
Spark和Hive这样的系统中, 有自增主键吗? 没有问题2: 为什么分布式系统中很少见自增主键? 因为分布式环境下数据在不同的节点中, 很难保证顺序
解决方案: 按照某一列去排序, 取前两条数据
遗留问题: 不容易在分组中取每一组的前两个
窗口函数在sql中的语法
1 | SELECT |
窗口函数在 SQL 中的完整语法如下
1 | function OVER (PARITION BY ... ORDER BY ... FRAME_TYPE BETWEEN ... AND ...) |
在 Spark 中, 使用 SQL 或者 DataFrame 都可以操作窗口
窗口函数和 GroupBy 最大的区别, 就是 GroupBy 的聚合对每一个组只有一个结果, 而窗口函数可以对每一条数据都有一个结果
说白了, 窗口函数其实就是根据当前数据, 计算其在所在的组中的统计数据
- 窗口函数会针对 每一个组中的每一条数据 进行统计聚合或者
rank, 一个组又称为一个Frame - 分组由两个字段控制,
Partition在整体上进行分组和分区 - 而通过
Frame可以通过 当前行 来更细粒度的分组控制